Diamonds Guide
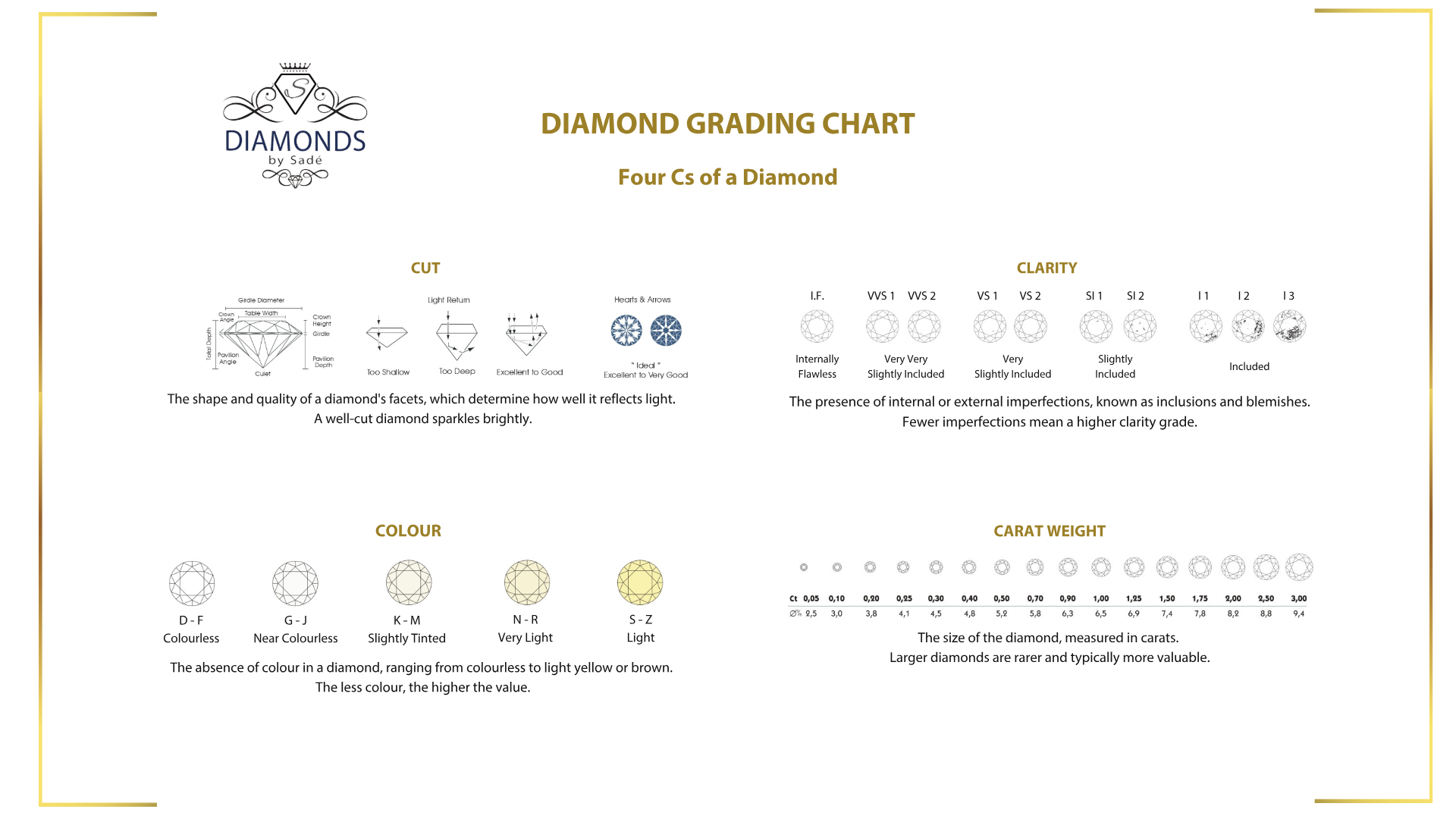
Diamonds are one of the most coveted gemstones, celebrated for their brilliance, durability, and timeless appeal. When selecting a diamond, understanding the "Four C’s" – Cut, Colour, Clarity, and Carat – is essential. These characteristics determine a diamond's beauty, quality, and value. Here's a detailed guide:
Cut
The cut of a diamond refers to how well it has been shaped and faceted by the jeweller. A well-cut diamond reflects light beautifully, enhancing its brilliance and sparkle. The quality of the cut is determined by its proportions, symmetry, and polish. Diamonds are graded on a scale ranging from Excellent to Poor.
- Tip: Opt for a high-quality cut, as it significantly impacts the diamond's overall appearance.
Colour
Colour measures how clear or tinted a diamond appears. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamonds on a scale from D (completely colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
- D-F: Colourless and the most sought-after.
- G-J: Near colourless, offering excellent value.
- K-Z: Increasing presence of noticeable colour.
- Tip: Colourless diamonds are ideal for those seeking the purest appearance, but near-colourless options can offer exceptional beauty at a more accessible price.
Clarity
Clarity assesses the presence of internal inclusions or external blemishes in a diamond. These imperfections are usually microscopic and do not affect the diamond's structural integrity. The GIA clarity scale includes:
- FL (Flawless): No inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification.
- IF (Internally Flawless): No inclusions, only minor surface blemishes.
- VVS: Inclusions are extremely difficult to detect.
- VS: Minor inclusions that are hard to see.
- SI: Noticeable inclusions under magnification, often invisible to the naked eye.
- I: Visible inclusions that may affect durability.
- Tip: For excellent value, consider diamonds in the VS or SI range, as imperfections are usually undetectable to the naked eye.
Carat
Carat refers to the weight of the diamond, with one carat equivalent to 200 milligrams. Larger diamonds are rarer and thus more expensive. However, carat weight is not the sole determinant of a diamond's visual size – the cut also plays a significant role.
- Tip: If size is important, consider diamonds just below whole carat weights (e.g., 0.90 carats instead of 1.00) for better value.
Additional Considerations
- Shape: Choose a diamond shape that complements your style. Popular options include round, princess, oval, and cushion cuts.
- Certification: Always purchase diamonds with a trusted certification, such as from the GIA or IGI, to ensure their quality and authenticity.
- Setting: The right setting can enhance a diamond’s brilliance and protect it from damage.
By understanding the Four C’s and exploring additional factors, you can select a diamond that aligns with your personal preferences, style, and budget, ensuring a piece of jewellery that will be cherished for a lifetime.
Gemstone Guide
Gemstones have captivated humanity for centuries, symbolising beauty, rarity, and meaning. Each gemstone is unique, with distinct characteristics that make it special. Whether you're selecting a gemstone for its aesthetic appeal, symbolic significance, or as a birthstone, understanding key factors can help you make an informed choice. Here's a comprehensive guide:
Types of Gemstones
Gemstones are broadly classified into two categories:
- Precious Gemstones
Diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds are considered precious due to their rarity, durability, and exceptional beauty. - Semi-Precious Gemstones
This category includes amethyst, topaz, garnet, aquamarine, and many more, valued for their vibrant colours and variety.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gemstone
1. Colour
The colour of a gemstone is its most striking feature, determined by three elements:
- Hue: The basic colour (e.g., blue, red, green).
- Tone: The lightness or darkness of the colour.
- Saturation: The intensity or purity of the colour.
2. Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of inclusions or blemishes inside or on the surface of a gemstone. While some gemstones may naturally have inclusions, clarity affects the stone's brilliance and value.
3. Cut
The cut of a gemstone influences its brilliance and how light interacts with it. Well-cut stones maximise colour and sparkle. Different shapes include round, oval, pear, cushion, and emerald cuts.
4. Carat Weight
Carat weight measures the size of a gemstone. Larger gemstones are rarer and typically more valuable, but personal preference and design suitability are also important.
5. Durability
Consider the hardness and toughness of the gemstone, especially for everyday wear. Diamonds and sapphires are very hard, while stones like opal and turquoise require more care.
Popular Gemstones
- Ruby: Known for its deep red colour and symbolic of love and passion.
- Sapphire: Famous for its rich blue hue and association with wisdom and nobility.
- Emerald: Valued for its vivid green colour and rarity.
- Amethyst: Appreciated for its purple tones and calming properties.
- Topaz: Comes in various colours, symbolising strength and intelligence.
Whether chosen for personal meaning, style, or as a gift, gemstones offer endless possibilities to express individuality and celebrate special moments.
Metal Guide
Platinum
Platinum is gaining popularity as a material for jewellery pieces, including wedding bands and engagement rings. Platinum is a sleek, silvery-white precious metal with an unmistakable shine. Platinum's natural strength is enhanced by adding a small percentage of another metal before it is crafted into jewellery. Jewellers may choose a range of metals to add to the alloy to strengthen it. We use cobalt as it is naturally hypoallergenic, like platinum, which ensures the rings are still a great option for people with metal allergies. Platinum is extremely durable and will not tarnish or corrode. Platinum jewellery comes at a higher price point than gold jewellery due to its incredible density, strength, and lustre.
Explore Platinum Engagement Rings
Rose Gold
Rose gold is a captivating precious metal, cherished for its warm and romantic blush-pink hue. This distinctive colour is achieved by alloying gold with copper, creating a unique tone that sets it apart from traditional yellow or white gold. The subtle pink shade of rose gold makes it an elegant and stylish choice, especially for those looking for something a little different.
Rose gold is particularly flattering on warmer skin tones, enhancing natural undertones with its soft and inviting glow. It is as versatile as it is beautiful, complementing both modern and vintage-inspired jewellery designs.
In terms of affordability, rose gold is comparable in price to yellow and white gold, making it a cost-effective alternative to platinum.
Whether chosen for its aesthetic appeal, durability, or value, rose gold continues to be a popular and stylish choice for jewellery lovers.
White Gold
White gold is a timeless and elegant choice, valued for its sleek, silvery-white appearance that exudes sophistication. Created by alloying gold with white metals such as palladium, silver, or nickel, white gold achieves its distinctive colour and enhanced strength. Its neutral tone makes it an incredibly versatile metal that pairs beautifully with a wide range of gemstones and complements both contemporary and classic jewellery designs.
To achieve its lustrous finish, white gold is typically plated with rhodium, a rare and highly reflective metal. This plating not only enhances its bright appearance but also provides an extra layer of protection against scratches and tarnishing. Over time, the rhodium plating may wear off, but it can be easily reapplied to restore the jewellery's original shine.
White gold is often chosen for its affordability compared to platinum while offering a similar aesthetic. It is a durable metal, well-suited for everyday wear, making it a popular option for engagement rings, wedding bands, and other fine jewellery.
Whether you're drawn to its modern appeal or its understated elegance, white gold remains a classic choice for those seeking beauty, durability, and versatility in their jewellery.
Yellow Gold
Yellow gold is a classic and timeless metal, celebrated for its rich, warm hue that evokes a sense of luxury and elegance. Known for its enduring appeal, yellow gold is made by alloying pure gold with other metals such as copper and silver, which not only enhances its strength but also allows it to maintain its signature golden tone. This metal has been cherished for centuries, symbolizing wealth, success, and status, making it a popular choice for significant life moments such as engagements, weddings, and heirloom pieces.
People are drawn to yellow gold for its rich, vibrant color, which stands out beautifully against all skin tones. Its timeless appeal makes it ideal for those who appreciate traditional aesthetics with a touch of opulence, as well as those looking for a piece that will never go out of style. Yellow gold is especially appealing to individuals who favor a classic, vintage look or those seeking a more warm, romantic feel in their jewellery.
In addition to its aesthetic beauty, yellow gold is a versatile choice that pairs seamlessly with a wide variety of gemstones, enhancing their colour and brilliance. It works equally well in modern, minimalist designs as it does in intricate, vintage-inspired settings. While yellow gold may require occasional polishing to maintain its shine, its enduring popularity and rich history make it a favourite for both new jewellery lovers and collectors alike. Whether you’re choosing a piece for everyday wear or a special occasion, yellow gold offers both beauty and a sense of heritage that few other metals can match.
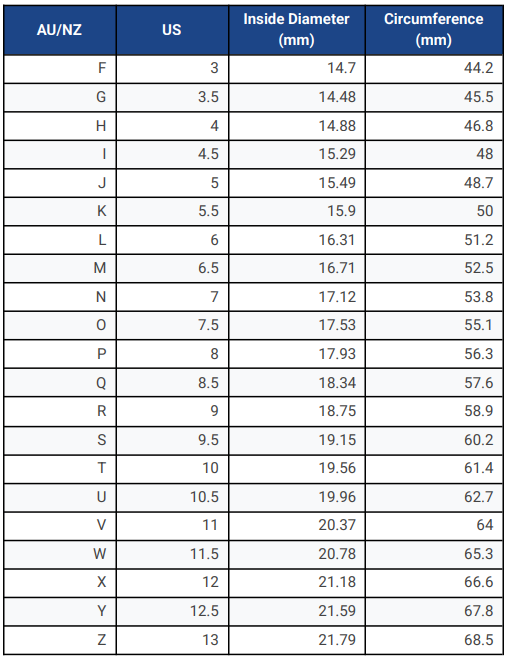
Ring Size Guide
To ensure the perfect fit, please refer to our ring size guide below:
Measuring Your Ring Size:
- Use a ring that fits: Compare the ring you want to purchase to a ring that already fits you.
- Measure the inside diameter: Measure the inside diameter of the ring in millimeters (mm).
- Use a ring sizer: You can purchase a ring sizer or use a printable ring sizer found online.
Ring Size Chart:
Tips:
- Measure your ring size at the end of the day, as fingers tend to be slightly larger.
- Consider the width of the band, as thicker bands may require a slightly larger size.
- If you’re still unsure, contact us for guidance.
- Measure your ring size at the end of the day, as fingers tend to be slightly larger.
- Consider the width of the band, as thicker bands may require a slightly larger size.
- If you’re still unsure, contact us for guidance.




